Relay Node
Prerequisites
You must first complete the steps in the Bare-Metal Server guide.
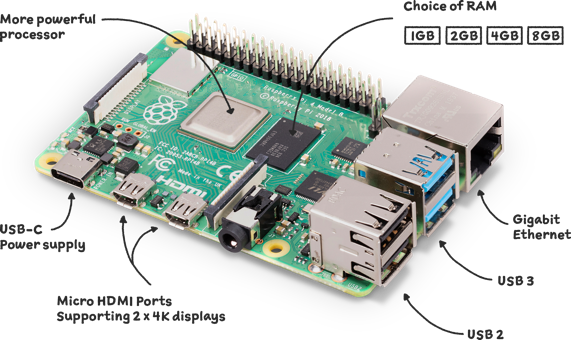
Raspberry Pi 4 Model B 8GB
Directory structure
Create the directories for the project:
mkdir -p ${HOME}/.local/bin && \
mkdir -p ${HOME}/pi-pool/files && \
mkdir -p ${HOME}/pi-pool/logs && \
mkdir -p ${HOME}/pi-pool/scripts && \
mkdir ${HOME}/tmp
We can visualise the project structure using the tree command:
sudo apt install tree
For example:
tree -da
You should see something like:
.
├── .local
│ ├── bin
├── pi-pool
│ ├── files
│ ├── logs
│ └── scripts
└── tmp
Configuration
Create a configuration file that will contain all the Cardano Node variables and settings:
nano .adaenv
And update it as follows:
NODE_CONFIG=mainnet
Then save (Ctrl+O) and exit (Ctrl+X) nano.
Source the file:
source ${HOME}/.adaenv
We want the .bashrc file to source the Cardano Node variables and settings:
echo . ~/.adaenv >> ${HOME}/.bashrc
Update the .adaenv file, add ~/.local/bin to the $PATH and create some bash variables:
cd .local/bin; echo "export PATH=\"$PWD:\$PATH\"" >> $HOME/.adaenv && \
echo export NODE_HOME=${HOME}/pi-pool >> ${HOME}/.adaenv && \
echo export NODE_PORT=5011 >> ${HOME}/.adaenv && \
echo export NODE_FILES=${HOME}/pi-pool/files >> ${HOME}/.adaenv && \
echo export TOPOLOGY='${NODE_FILES}'/'${NODE_CONFIG}'-topology.json >> ${HOME}/.adaenv && \
echo export DB_PATH='${NODE_HOME}'/db >> ${HOME}/.adaenv && \
echo export CONFIG='${NODE_FILES}'/'${NODE_CONFIG}'-config.json >> ${HOME}/.adaenv && \
echo export NODE_BUILD_NUM=$(curl https://hydra.iohk.io/job/Cardano/iohk-nix/cardano-deployment/latest-finished/download/1/index.html | grep -e "build" | sed 's/.*build\/\([0-9]*\)\/download.*/\1/g') >> ${HOME}/.adaenv && \
echo export CARDANO_NODE_SOCKET_PATH="${HOME}/pi-pool/db/socket" >> ${HOME}/.adaenv
Check the updated .adaenv file:
cat ${HOME}/.adaenv
You should see something like:
NODE_CONFIG=mainnet
export PATH="/home/ada/.local/bin:$PATH"
export NODE_HOME=/home/ada/pi-pool
export NODE_PORT=5011
export NODE_FILES=/home/ada/pi-pool/files
export TOPOLOGY=${NODE_FILES}/${NODE_CONFIG}-topology.json
export DB_PATH=${NODE_HOME}/db
export CONFIG=${NODE_FILES}/${NODE_CONFIG}-config.json
export NODE_BUILD_NUM=14528927
export CARDANO_NODE_SOCKET_PATH=/home/ada/pi-pool/db/socket
Source the updated files:
source ${HOME}/.bashrc; source ${HOME}/.adaenv
It is important to remember that if you change a variable or a setting in the .adaenv configuration file, then you must
reinitialise the values by sourcing the file. This also applies to changes that you make to any other configuration or
topology files. You must also restart the Cardano Node after any changes.
Download the node config files
Download the node config files:
cd $NODE_FILES
wget -N https://hydra.iohk.io/build/${NODE_BUILD_NUM}/download/1/${NODE_CONFIG}-config.json
wget -N https://hydra.iohk.io/build/${NODE_BUILD_NUM}/download/1/${NODE_CONFIG}-byron-genesis.json
wget -N https://hydra.iohk.io/build/${NODE_BUILD_NUM}/download/1/${NODE_CONFIG}-shelley-genesis.json
wget -N https://hydra.iohk.io/build/${NODE_BUILD_NUM}/download/1/${NODE_CONFIG}-alonzo-genesis.json
wget -N https://hydra.iohk.io/build/${NODE_BUILD_NUM}/download/1/${NODE_CONFIG}-topology.json
wget -N https://raw.githubusercontent.com/input-output-hk/cardano-node/master/cardano-submit-api/config/tx-submit-mainnet-config.yaml
Build the Cardano ARM binaries
Download the Cardano ARM binaries
The cardano-node, cardano-cli and cardano-submit-api ARM binaries are built by an IOHK engineer in his spare time. Please consider delegating to the zw3rk pool.
cd ${HOME}/tmp
wget -O 1_35_3.zip https://github.com/armada-alliance/cardano-node-binaries/blob/main/static-binaries/1_35_3.zip?raw=true
unzip *.zip
mv cardano-node/cardano-* ${HOME}/.local/bin
rm -r *
cd ${HOME}
Confirm that the binaries are in the $USER's (ada) $PATH:
cardano-node version && \
cardano-cli version && \
which cardano-submit-api
You should see something like:
$ cardano-node version
cardano-node 1.35.3 - linux-aarch64 - ghc-8.10
git rev 0000000000000000000000000000000000000000
$ cardano-cli version
cardano-cli 1.35.3 - linux-aarch64 - ghc-8.10
git rev 0000000000000000000000000000000000000000
$ which cardano-submit-api
/home/ada/.local/bin/cardano-submit-api
Glasgow Haskell Compiler
The Cardano binaries are implemented in Haskell which is a polymorphically statically typed, lazy, purely functional programming language. The Cardano executable binaries are built using Cabal (a system for building and packaging Haskell libraries and programs) and the Glasgow Haskell Compiler (GHC).
To make an executable program, GHC compiles the source code and then links it with a non-trivial runtime system, which handles storage management, thread scheduling, profiling, and so on.
We can determine the default runtime system (RTS) parameters that the node has been complied with, using the following command:
cardano-node +RTS --info
You should see something like:
[("GHC RTS", "YES")
,("GHC version", "8.10.7")
,("RTS way", "rts_thr")
,("Build platform", "x86_64-unknown-linux")
,("Build architecture", "x86_64")
,("Build OS", "linux")
,("Build vendor", "unknown")
,("Host platform", "x86_64-unknown-linux")
,("Host architecture", "x86_64")
,("Host OS", "linux")
,("Host vendor", "unknown")
,("Target platform", "aarch64-unknown-linux")
,("Target architecture", "aarch64")
,("Target OS", "linux")
,("Target vendor", "unknown")
,("Word size", "64")
,("Compiler unregisterised", "NO")
,("Tables next to code", "YES")
,("Flag -with-rtsopts", "-T -I0 -A16m -N2 --disable-delayed-os-memory-return")]
So the default RTS parameters are:
-T -I0 -A16m -N2 --disable-delayed-os-memory-return
Runtime system options
The RTS has a lot of options to control its behaviour. For example, you can change the context-switch interval, the default size of the heap, and enable heap profiling.
Setting the runtime system options
You can set the RTS options by using the GHCRTS environment variable.
Open the .bashrc file:
nano $HOME/.bashrc
Add the following line to the bottom of the file:
export GHCRTS='-A64M -AL128M -F1.1 -H3500M -I0.1 -Iw3600 -N2 -n4m -O3500M --disable-delayed-os-memory-return'
Then save (Ctrl+O) and exit (Ctrl+X) nano.
Source the file:
source $HOME/.bashrc
Runtime statistics
The -S RTS option produces information about each and every garbage collection:
export GHCRTS='-A64M -AL128M -F1.1 -H3500M -I0.1 -Iw3600 -N2 -n4m -O3500M --disable-delayed-os-memory-return -S'
The output is sent to stderr.
To further reduce memory and cpu usage set "TraceMemPool" to "false" in the ${NODE_CONFIG}-config.json file:
cd $NODE_FILES
sed -i ${NODE_CONFIG}-config.json \
-e "s/TraceMempool\": true/TraceMempool\": false/g"
Systemd service configuration
Create the cardano-node startup script:
nano ${HOME}/.local/bin/cardano-service
And update it as follows:
#!/bin/bash
. /home/ada/.adaenv
cardano-node run \
--topology ${TOPOLOGY} \
--database-path ${DB_PATH} \
--socket-path ${CARDANO_NODE_SOCKET_PATH} \
--port ${NODE_PORT} \
--config ${CONFIG}
Then save (Ctrl+O) and exit (Ctrl+X) nano.
Make the script executable:
chmod +x ${HOME}/.local/bin/cardano-service
Create the cardano-node systemd unit file:
sudo nano /etc/systemd/system/cardano-node.service
And update it as follows:
# The Cardano Node Service (part of systemd)
# file: /etc/systemd/system/cardano-node.service
[Unit]
Description = Cardano node service
Wants = network-online.target
After = network-online.target
[Service]
User = ada
Type = simple
WorkingDirectory= /home/ada/pi-pool
ExecStart = /bin/bash -c "PATH=/home/ada/.local/bin:$PATH exec /home/ada/.local/bin/cardano-service"
KillSignal=SIGINT
RestartKillSignal=SIGINT
TimeoutStopSec=10
LimitNOFILE=32768
Restart=always
RestartSec=10
EnvironmentFile=-/home/ada/.adaenv
[Install]
WantedBy= multi-user.target
Then save (Ctrl+O) and exit (Ctrl+X) nano.
Create the cardano-submit-api startup script:
nano ${HOME}/.local/bin/cardano-submit-service
And update it as follows:
#!/bin/bash
. /home/ada/.adaenv
cardano-submit-api \
--socket-path ${CARDANO_NODE_SOCKET_PATH} \
--port 8090 \
--config /home/ada/pi-pool/files/tx-submit-mainnet-config.yaml \
--listen-address 0.0.0.0 \
--mainnet
Then save (Ctrl+O) and exit (Ctrl+X) nano.
Make the script executable:
chmod +x ${HOME}/.local/bin/cardano-submit-service
Create the cardano-submit-api systemd unit file:
sudo nano /etc/systemd/system/cardano-submit.service
And update it as follows:
# The Cardano Submit Service (part of systemd)
# file: /etc/systemd/system/cardano-submit.service
[Unit]
Description = Cardano submit service
Wants = network-online.target
After = network-online.target
[Service]
User = ada
Type = simple
WorkingDirectory= /home/ada/pi-pool
ExecStart = /bin/bash -c "PATH=/home/ada/.local/bin:$PATH exec /home/ada/.local/bin/cardano-submit-service"
KillSignal=SIGINT
RestartKillSignal=SIGINT
TimeoutStopSec=10
LimitNOFILE=32768
Restart=always
RestartSec=10
EnvironmentFile=-/home/ada/.adaenv
[Install]
WantedBy= multi-user.target
Then save (Ctrl+O) and exit (Ctrl+X) nano.
Reload systemd:
sudo systemctl daemon-reload
Now we can update the .adaenv file:
nano $HOME/.adaenv
Add the following lines to the bottom of the file:
cardano-service() {
sudo systemctl "$1" cardano-node.service
}
cardano-submit() {
sudo systemctl "$1" cardano-submit.service
}
Then save (Ctrl+O) and exit (Ctrl+X) nano.
Source the file:
source ${HOME}/.adaenv
What we just did was create a couple of utility functions that make it easier to control the Cardano Node and the Cardano Submit API.
For example:
cardano-service enable
cardano-service start
cardano-service status
cardano-service stop
Syncing to the blockchain
Starting the cardano-node will begin the process of syncing to the blockchain.
This is going to take a quite a while, the /db folder is about 80GB in size right now.
.
├── .local
│ ├── bin
├── pi-pool
│ ├── db
│ │ ├── immutable
│ │ ├── ledger
│ │ └── volatile
│ ├── files
│ ├── logs
│ └── scripts
└── tmp
Start the cardano-node:
cardano-service enable
cardano-service start
You only need to synchronise your first node, after that you can use the Synology DSM's File Station to copy the database directory.
Connecting with peers
topologyUpdater is a Guild Operators helper script that enables nodes to connect with other nodes.
Download the script:
cd $NODE_HOME/scripts
wget https://raw.githubusercontent.com/cardano-community/guild-operators/master/scripts/cnode-helper-scripts/topologyUpdater.sh
Open the topologyUpdater.sh file:
nano topologyUpdater.sh
Lower the number of MAX_PEERS to 6 and add your custom peers (e.g., the IP address and port number of your Core Node):
...
MAX_PEERS=6
CUSTOM_PEERS="192.168.102.3,3000"
Then save (Ctrl+O) and exit (Ctrl+X) nano.
Make the script executable:
chmod +x topologyUpdater.sh
Create a cron job
Create a cron job that will run the topologyUpdater script once an hour:
crontab -e
Add the following lines to the bottom of the file:
SHELL=/bin/bash
PATH=/home/ada/.local/bin:/usr/bin:/bin:/usr/sbin:/sbin:/usr/local/bin
33 * * * * . $HOME/.adaenv; $HOME/pi-pool/scripts/topologyUpdater.sh
Then save (Ctrl+O) and exit (Ctrl+X) nano.
Monitoring
gLiveView
gLiveView is a Guild Operators monitoring tool that displays crucial node status information.
Download the tool:
cd $NODE_HOME/scripts
wget https://raw.githubusercontent.com/cardano-community/guild-operators/master/scripts/cnode-helper-scripts/env
wget https://raw.githubusercontent.com/cardano-community/guild-operators/master/scripts/cnode-helper-scripts/gLiveView.sh
Add a line sourcing the .adaenv file to the top of the Guild Operators common environment
file (called env) and adjust some paths:
sed -i env \
-e "/#CNODEBIN/i. ${HOME}/.adaenv" \
-e "s/\#CNODE_HOME=\"\/opt\/cardano\/cnode\"/CNODE_HOME=\"\${HOME}\/pi-pool\"/g" \
-e "s/\#CNODE_PORT=6000"/CNODE_PORT=\"'${NODE_PORT}'\""/g" \
-e "s/\#CONFIG=\"\${CNODE_HOME}\/files\/config.json\"/CONFIG=\"\${NODE_FILES}\/"'${NODE_CONFIG}'"-config.json\"/g" \
-e "s/\#TOPOLOGY=\"\${CNODE_HOME}\/files\/topology.json\"/TOPOLOGY=\"\${NODE_FILES}\/"'${NODE_CONFIG}'"-topology.json\"/g" \
-e "s/\#LOG_DIR=\"\${CNODE_HOME}\/logs\"/LOG_DIR=\"\${CNODE_HOME}\/logs\"/g"
Make the script executable:
chmod +x gLiveView.sh
A node must synchronise to (at least) epoch 208 (Shelley launch) before gLiveView can start tracking the synchronisation process.
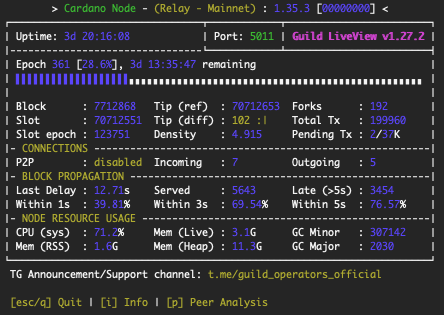
Run gLiveView:
cd $NODE_HOME/scripts
./gLiveView.sh
You should see something like:
Prometheus
Install Prometheus Node Exporter:
sudo apt install -y prometheus-node-exporter
Run the following command to update the IP address for 'hasPrometheus' from 127.0.0.1 to 0.0.0.0 and enable
'TraceBlockFetchDecisions' in the ${NODE_CONFIG}-config.json file:
cd $NODE_FILES
sed -i ${NODE_CONFIG}-config.json \
-e "s/127.0.0.1/0.0.0.0/g" \
-e "s/TraceBlockFetchDecisions\": false/TraceBlockFetchDecisions\": true/g"
Now we can update the .adaenv file:
nano $HOME/.adaenv
Add the following lines to the bottom of the file:
prometheus-node-exporter() {
sudo systemctl "$1" prometheus-node-exporter.service
}
Then save (Ctrl+O) and exit (Ctrl+X) nano.
Source the file:
source ${HOME}/.adaenv
What we just did was create a utility function that makes it easier to control the Prometheus Node Exporter.
For example:
prometheus-node-exporter enable
prometheus-node-exporter start
prometheus-node-exporter status
prometheus-node-exporter stop
prometheus-node-exporter disable
Start the prometheus-node-exporter:
prometheus-node-exporter enable
prometheus-node-exporter start
Resources
- Haskell docs: Runtime system (RTS) options
- Glasgow Haskell Compiler User's Guide: Advice on: sooner, faster, smaller, thriftier
- Cardano forum - ANFA July 21: Solving the Cardano node huge memory usage problem
- Cardano forum - ANFA December 21: Solving the Cardano node huge memory usage problem
- GitHub input-output-hk daedalus: Drastically reduce cardano-node memory usage by setting RTS params